Your cart is currently empty!
OpenAvatarChat: A Detailed Explanation of System Architecture and Handler Collaboration Mechanism
BY

1. Overall Architecture
1.1 System Hierarchical Structure
OpenAvatarChat adopts a layered architecture, divided into three levels from top to bottom:
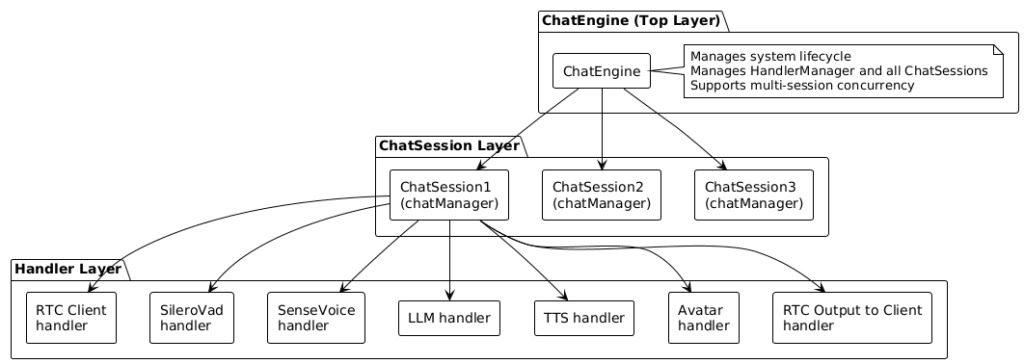
Architecture Description:
1. ChatEngine (Top Layer)
▪️ The core of the system, managing the entire chat engine
▪️ Responsible for initialization, configuration loading, and Handler management
▪️ Supports concurrent multi-session operation, with each session running independently
2. ChatSession (Middle Layer)
▪️ Corresponds to a user session (one WebRTC connection)
▪️ Manages all Handler instances within the session
▪️ Manages data flow, threads, and queues
3. Handler (Bottom Layer)
▪️ Functional modules responsible for specific task processing
▪️ Includes: RTC client, VAD, ASR, LLM, TTS, Avatar, etc.
▪️ Each Handler creates an independent instance when the session starts
1.2 Core Component Description
ChatEngine (src/chat_engine/chat_engine.py)
Responsibilities:
▪️ System initialization and management
▪️ Creation and initialization of HandlerManager
▪️ Creation and destruction of sessions
▪️ Management of concurrent multi-session operation
Key Methods:
def initialize(engine_config, app=None, ui=None):
# Initialize HandlerManager
# Load all Handlers
# Set up the client Handler
def create_client_session(session_info, client_handler):
# Create a new ChatSession
# Prepare the Handler environment
# Return the session and Handler environment
def stop_session(session_id):
# Stop and destroy the sessionHandlerManager (src/chat_engine/core/handler_manager.py)
Responsibilities:
▪️ Dynamically load Handler modules from configuration files
▪️ Register Handler instances
▪️ Manage Handler lifecycle
Key Data Structure:
handler_registries = {
"RtcClient": HandlerRegistry(
base_info=HandlerBaseInfo(...),
handler=RtcClient instance,
handler_config=configuration object
),
"SileroVad": HandlerRegistry(...),
...
}ChatSession (src/chat_engine/core/chat_session.py)
Responsibilities:
▪️ Manage data flow for a single session
▪️ Create and manage Handler instances
▪️ Data routing and distribution
▪️ Thread management
Key Data Structure:
# Data routing table: Data type → Handler input queue
data_sinks = {
ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO: [
DataSink(owner="SileroVad", sink_queue=vad_queue),
],
ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT: [
DataSink(owner="LLM_Bailian", sink_queue=llm_queue),
],
}
# Handler records: Handler name → Handler environment
handlers = {
"SileroVad": HandlerRecord(env=HandlerEnv(...)),
...
}2. Data Flow Process
2.1 Complete Data Flow Architecture Diagram
The complete data flow is as follows:

2.2 Detailed Data Flow Process
Step 1: Client Input
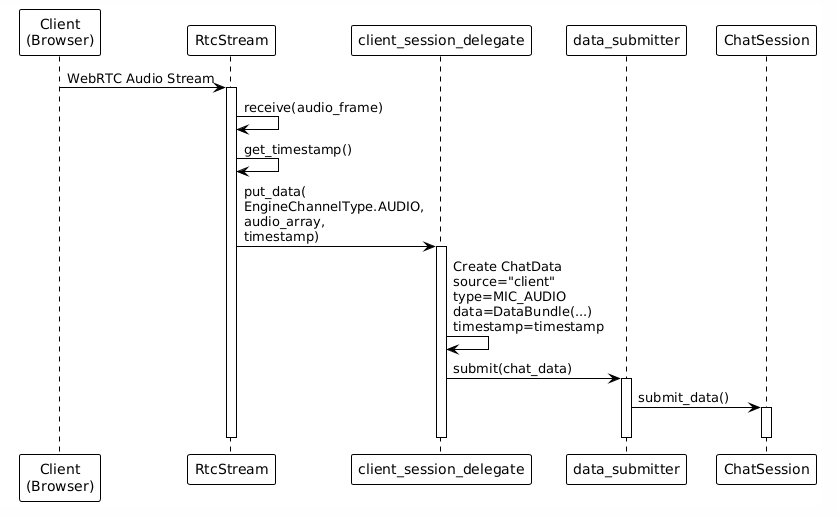
Step 2: Data Distribution (Subscription Distribution)
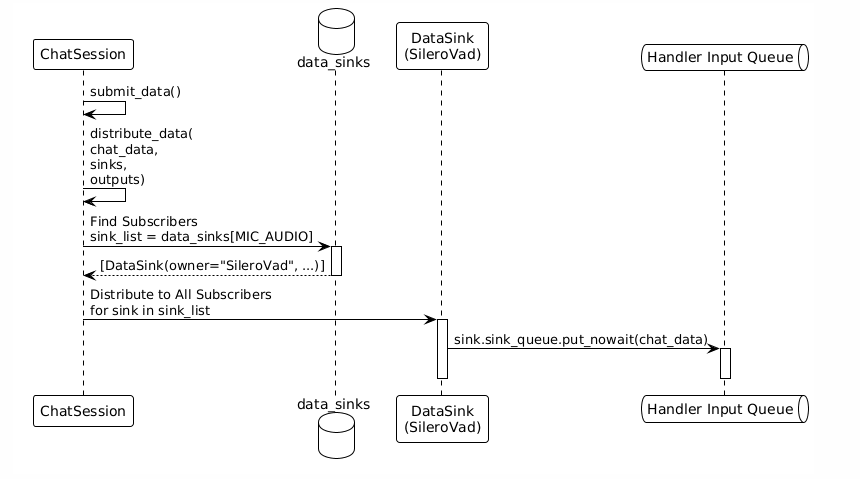
Key Mechanisms:
▪️ data_sinks is a mapping table from data types to Handler input queues.
▪️ The system automatically finds all subscribers based on the data type.
▪️ Data is simultaneously distributed to all Handlers that have subscribed to that data type.
Step 3: Handler Processing
Each Handler has an independent processing thread that reads data from its own input queue:
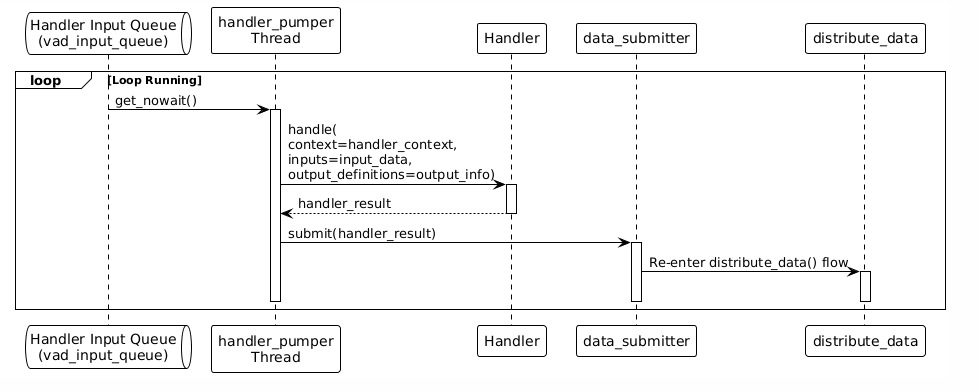
Step 4: Chained Data Flow
Data automatically forms a processing chain based on the input and output definitions of the Handlers:
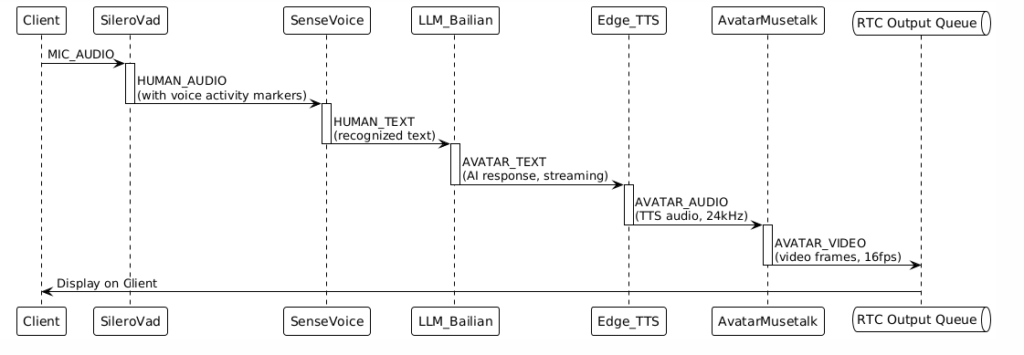
Step 5: Client Output
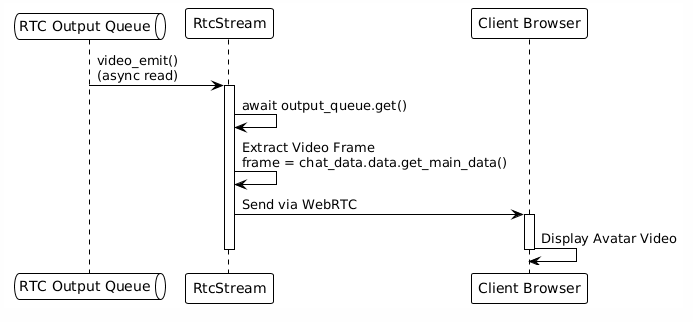
2.3 Key Data Structures: Queues and Routing
Input Queues:
# Client input queues (created by RTC Client Handler)
input_queues = {
EngineChannelType.AUDIO: asyncio.Queue(),
EngineChannelType.VIDEO: asyncio.Queue(),
EngineChannelType.TEXT: asyncio.Queue(),
}Handler Input Queues:
# Each Handler has its own input queue
vad_input_queue = queue.Queue() # Input queue for SileroVad
asr_input_queue = queue.Queue() # Input queue for SenseVoice
llm_input_queue = queue.Queue() # Input queue for LLM_Bailian
tts_input_queue = queue.Queue() # Input queue for Edge_TTS
avatar_input_queue = queue.Queue() # Input queue for AvatarMusetalkData Routing Table (data_sinks):
# Data type → List of Handlers that subscribe to this type
data_sinks = {
ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO: [
DataSink(owner="SileroVad", sink_queue=vad_input_queue),
],
ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO: [
DataSink(owner="SenseVoice", sink_queue=asr_input_queue),
],
ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT: [
DataSink(owner="LLM_Bailian", sink_queue=llm_input_queue),
],
ChatDataType.AVATAR_TEXT: [
DataSink(owner="Edge_TTS", sink_queue=tts_input_queue),
],
ChatDataType.AVATAR_AUDIO: [
DataSink(owner="AvatarMusetalk", sink_queue=avatar_input_queue),
],
}Output Queue Mapping:
# (Handler Name, Data Type) → Output Queue
outputs = {
("AvatarMusetalk", ChatDataType.AVATAR_VIDEO): DataSink(
sink_queue=output_queues[EngineChannelType.VIDEO]
),
}3. The Essence of Handler
3.1 What is a Handler?
▪️ A Handler is an independent functional module, and each Handler is responsible for a specific task:
▪️ RTC Client Handler: Manages WebRTC connections, receives user input, and sends output
▪️ SileroVad Handler: Voice Activity Detection (VAD), detects whether the user is speaking
▪️ SenseVoice Handler: Speech Recognition (ASR), converts speech into text
▪️ LLM Handler: Large Language Model, generates response text
▪️ TTS Handler: Text-to-Speech (TTS), converts text into audio
▪️ Avatar Handler: Avatar driving, generates video from audio
3.2 The Nature of a Handler: Independent Threads
Key Understanding: Each Handler creates an independent thread when the session starts.
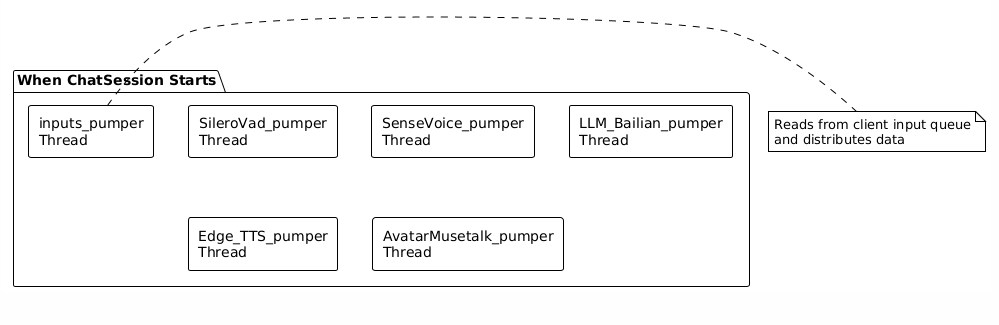
Thread Operation Mode:
# Core loop of the handler_pumper thread
def handler_pumper(session_context, handler_env, sinks, outputs):
shared_states = session_context.shared_states
input_queue = handler_env.input_queue # Handler's input queue
while shared_states.active: # Continue running while the session is active
try:
# 1. Read data from the input queue
input_data = input_queue.get_nowait()
except queue.Empty:
time.sleep(0.03) # Sleep for 30ms when the queue is empty
continue
# 2. Call the Handler to process the data
handler_result = handler_env.handler.handle(
handler_env.context,
input_data,
handler_env.output_info
)
# 3. Submit the processed result
ChatDataSubmitter.submit(handler_result)
│
└─→ distribute_data() # Distribute to the next Handler3.3 The Lifecycle of a Handler
Stage 1: Load (load)
When the system starts, each Handler executes a load:
handler.load(engine_config, handler_config)Purpose:
▪️ Load model files
▪️ Initialize global resources
▪️ Prepare the Handler runtime environment
Examples:
▪️ SileroVad: Load the VAD model
▪️ SenseVoice: Load the ASR model
▪️ LLM: Initialize API client
▪️ Avatar: Load the avatar model
Stage 2: Create Context (create_context)
When each session is created, an independent context is created for each Handler:
handler_context = handler.create_context(session_context, handler_config)
Purpose:
▪️ Create session-related states
▪️ For example: LLM creates conversation history, ASR creates an audio buffer
Stage 3: Handle (handle)
During the session, the Handler continuously processes data:
handler_result = handler.handle(context, inputs, output_definitions)
Features:
▪️ Each Handler runs in its own thread
▪️ It reads data from its own input queue
▪️ After processing, it outputs the result
Stage 4: Destroy Context (destroy_context)
When the session ends, the Handler context is cleaned up:
handler.destroy_context(handler_context)
Purpose:
▪️ Release session-related resources
▪️ Clean up state data
3.4 Interface Definition of Handlers
All Handlers inherit from HandlerBase and must implement the following interfaces:
class HandlerBase(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def load(self, engine_config, handler_config):
"""Load the Handler (e.g., load models)"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def create_context(self, session_context, handler_config):
"""Create Handler context"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def handle(self, context, inputs, output_definitions):
"""Process input data"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_handler_detail(self, session_context, context):
"""Declare input and output data types"""
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={...}, # Input type definitions
outputs={...} # Output type definitions
)
@abstractmethod
def destroy_context(self, context):
"""Destroy Handler context"""
pass
3.5 Key Method of Handler: get_handler_detail
This is the key method for interaction between the Handler and the system. The Handler declares its inputs and outputs through this method:
def get_handler_detail(self, session_context, context) -> HandlerDetail:
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={
ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(
type=ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO,
# Other configurations...
)
},
outputs={
ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(
type=ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO,
definition=output_definition,
)
}
)
How the System Uses It:
1. During the prepare_handler() stage, the system calls get_handler_detail().
2. Based on the returned inputs, the system creates a data routing table:
for input_type, input_info in io_detail.inputs.items():
sink_list = data_sinks.setdefault(input_type, [])
data_sink = DataSink(
owner=handler_name,
sink_queue=handler_input_queue
)
sink_list.append(data_sink)3. When data of that type arrives, the system automatically distributes it to the Handler’s input queue.
4. Handler Collaborative Mechanism
4.1 Data Subscription Mechanism
Core Idea: Handlers “subscribe” to data by declaring input types, and the system automatically establishes data routing.
Establishing Subscription Relationships
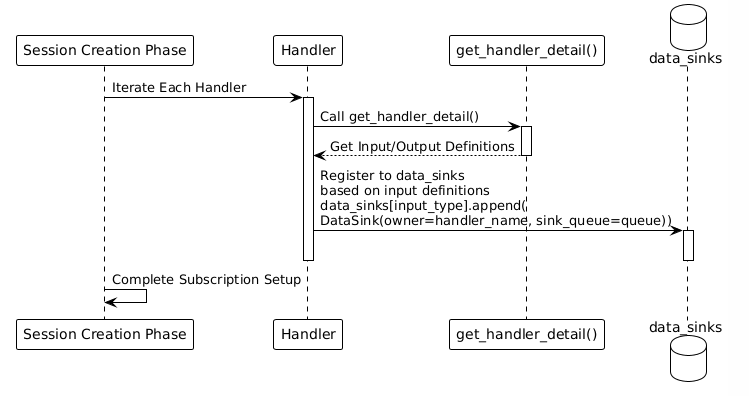
Subscription Example
For example, in the glut3.yaml configuration:
# SileroVad subscribes to MIC_AUDIO
data_sinks[ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO] = [
DataSink(owner="SileroVad", sink_queue=vad_queue),
]
# SenseVoice subscribes to HUMAN_AUDIO (SileroVad's output)
data_sinks[ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO] = [
DataSink(owner="SenseVoice", sink_queue=asr_queue),
]
# LLM_Bailian subscribes to HUMAN_TEXT (SenseVoice's output)
data_sinks[ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT] = [
DataSink(owner="LLM_Bailian", sink_queue=llm_queue),
]
# Edge_TTS subscribes to AVATAR_TEXT (LLM's output)
data_sinks[ChatDataType.AVATAR_TEXT] = [
DataSink(owner="Edge_TTS", sink_queue=tts_queue),
]
# AvatarMusetalk subscribes to AVATAR_AUDIO (TTS's output)
data_sinks[ChatDataType.AVATAR_AUDIO] = [
DataSink(owner="AvatarMusetalk", sink_queue=avatar_queue),
]
4.2 Data Distribution Mechanism (Subscription Distribution)
When data arrives, the system automatically distributes it through distribute_data():
def distribute_data(data: ChatData, sinks, outputs):
# 1. Check if it's the final output (directly sent to the client)
source_key = (data.source, data.type)
if source_key in outputs:
outputs[source_key].sink_queue.put_nowait(data)
# 2. Find all Handlers subscribed to this data type
sink_list = sinks.get(data.type, [])
# 3. Distribute to all subscribers
for sink in sink_list:
if sink.owner == data.source:
continue # Skip the data source itself
sink.sink_queue.put_nowait(data) # Put into Handler's input queue
Key Points:
▪️ Data is automatically routed based on type.
▪️ A piece of data can be distributed to multiple subscribers simultaneously.
▪️ Handlers are completely decoupled and unaware of each other’s existence.
4.3 Handler Parallel Processing Mechanism
Parallel Execution
All Handler threads run simultaneously without blocking each other:
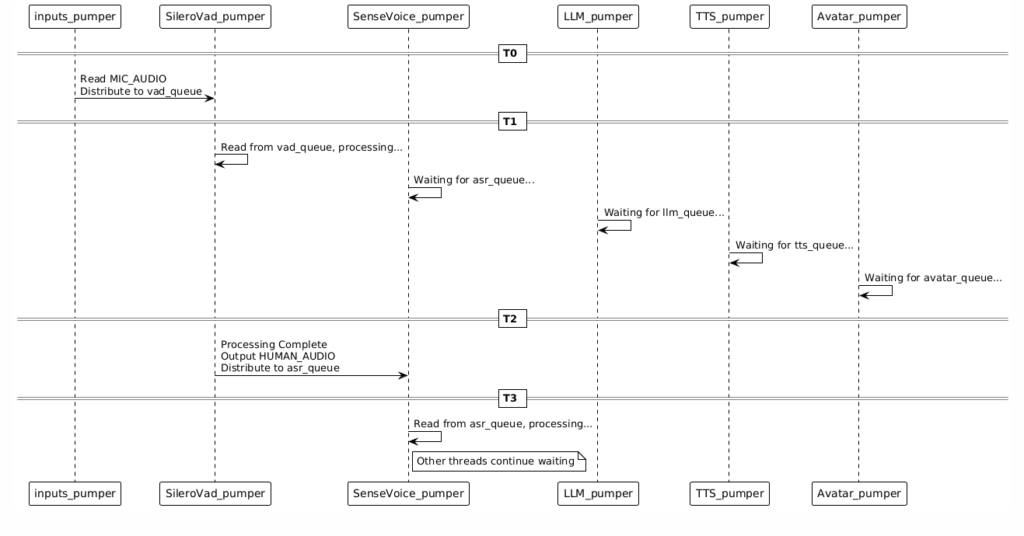
Data Flow Sequence Guarantee
Although Handlers run in parallel, the data flow is sequential:
MIC_AUDIO → HUMAN_AUDIO → HUMAN_TEXT → AVATAR_TEXT → AVATAR_AUDIO → AVATAR_VIDEO
Why the Sequence is Guaranteed
1. Data Type Driven:
▪️ SileroVad outputs HUMAN_AUDIO
▪️ SenseVoice subscribes to HUMAN_AUDIO (not MIC_AUDIO)
▪️ SenseVoice only receives data when HUMAN_AUDIO is produced
2. Queue Buffering:
▪️ Each Handler has its own input queue.
▪️ The queue automatically buffers data to ensure the sequence.
3. VAD’s Speech End Marker:
▪️ VAD outputs the human_speech_end marker during processing.
▪️ ASR waits for this marker before performing inference.
▪️ This ensures that a complete speech segment is processed.
4.4 Decoupling of Handlers
Complete Decoupling
Handlers do not communicate directly with each other, only interact through data types:
❌ Incorrect Way (Tightly Coupled):
SileroVad → Direct Call → SenseVoice.handle()
✅ Correct Way (Decoupled):
SileroVad → Outputs HUMAN_AUDIO → System Distributes → SenseVoice Input Queue
Benefits of Decoupling
1. Easy to Extend: Adding a new Handler only requires declaring input/output without modifying existing Handlers.
2. Flexible Combination: Handlers can be flexibly combined through configuration files.
3. Easy to Test: Each Handler can be tested independently.
4. Easy to Maintain: Handlers have clear responsibilities and do not interfere with each other.
4.5 Session End Mechanism
Shared Flag Control
All threads share a flag: shared_states.active
# While the session is running
shared_states.active = True
# All threads loop and check
while shared_states.active:
# Process data
...
# When the session ends
shared_states.active = False
# All threads automatically exit the loop
End Process
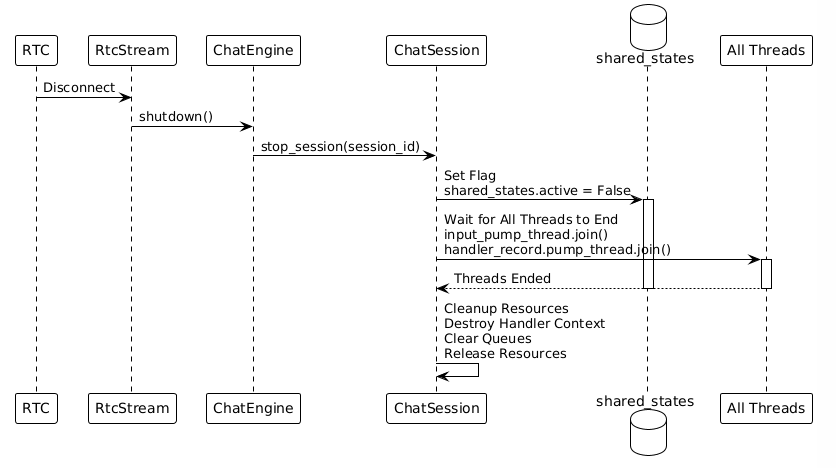
5. Detailed Explanation of Handlers
5.1 RTC Client Handler
Function: Manages WebRTC connections and handles bidirectional communication with the client.
Input: Client audio/video/text (received via WebRTC)
Output: Avatar video/audio (sent via WebRTC)
Key Code Locations:
▪️ src/handlers/client/rtc_client/client_handler_rtc.py
▪️ src/service/rtc_service/rtc_stream.py
Workflow:
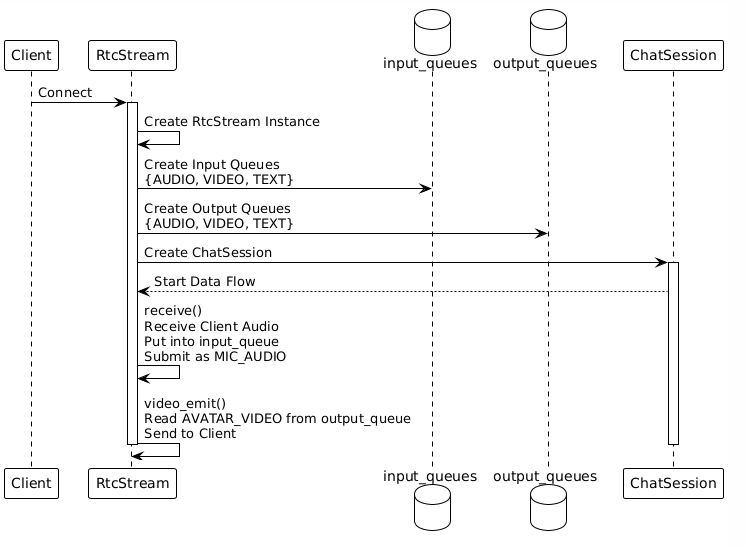
5.2 SileroVad Handler (Voice Activity Detection)
Function: Detects whether the user is speaking and filters out silence.
Input: ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO (raw audio)
Output: ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO (human speech audio, with speech activity markers)
Key Code Location: src/handlers/vad/silerovad/vad_handler_silero.py
Key Methods:
def get_handler_detail(self, ...):
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={
ChatDataType.MIC_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(...)
},
outputs={
ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(...)
}
)
def handle(self, context, inputs, output_definitions):
# 1. Extract audio from input
audio_data = inputs.data.get_main_data()
# 2. VAD model inference
is_speech = self.model(audio_data)
# 3. If speech is detected, output HUMAN_AUDIO
if is_speech:
yield ChatData(type=HUMAN_AUDIO, data=audio_data)
Features:
▪️ Real-time processing with streaming output
▪️ Output contains human_speech_start and human_speech_end markers
▪️ ASR relies on these markers to determine when to perform recognition
5.3 SenseVoice Handler (Speech Recognition)
Function: Converts speech to text.
Input: ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO (human speech audio)
Output: ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT (recognized text)
Key Code Location: src/handlers/asr/sensevoice/asr_handler_sensevoice.py
Key Methods:
def get_handler_detail(self, ...):
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={
ChatDataType.HUMAN_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(...)
},
outputs={
ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT: HandlerDataInfo(...)
}
)
def handle(self, context, inputs, output_definitions):
# 1. Accumulate audio data
context.audio_buffer.append(inputs.data.get_main_data())
# 2. Check if there is a human_speech_end marker
if inputs.data.has_meta('human_speech_end'):
# 3. Perform ASR inference
text = self.model(context.audio_buffer)
# 4. Output recognized text
yield ChatData(type=HUMAN_TEXT, data=text)
# 5. Clear the buffer
context.audio_buffer.clear()
Features:
▪️ Accumulates audio and waits for the speech end marker
▪️ Performs ASR on complete speech segments
▪️ Text format output: <|zh|><|NEUTRAL|><|Speech|><|woitn|>你好
5.4 LLM Handler (Large Language Model)
Function: Understands user input and generates response text.
Input: ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT (user text)
Output: ChatDataType.AVATAR_TEXT (AI response text)
Key Code Location: src/handlers/llm/openai_compatible/llm_handler_openai_compatible.py
Key Methods:
def get_handler_detail(self, ...):
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={
ChatDataType.HUMAN_TEXT: HandlerDataInfo(...)
},
outputs={
ChatDataType.AVATAR_TEXT: HandlerDataInfo(...)
}
)
def handle(self, context, inputs, output_definitions):
# 1. Update conversation history
context.history.add_user_message(inputs.data.get_main_data())
# 2. Call the LLM API (streaming)
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model_name,
messages=context.history.get_messages(),
stream=True
)
# 3. Stream the output text
for chunk in response:
text = chunk.choices[0].delta.content
if text:
yield ChatData(type=AVATAR_TEXT, data=text)
Features:
▪️ Maintains conversation history
▪️ Supports streaming output
▪️ Configurable for different LLM models (Bailian, OpenAI compatible, etc.)
5.5 Edge_TTS Handler (Text-to-Speech)
Function: Converts text to speech.
Input: ChatDataType.AVATAR_TEXT (AI response text)
Output: ChatDataType.AVATAR_AUDIO (generated audio)
Key Code Location: src/handlers/tts/edgetts/tts_handler_edgetts.py
Key Methods:
def get_handler_detail(self, ...):
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={
ChatDataType.AVATAR_TEXT: HandlerDataInfo(...)
},
outputs={
ChatDataType.AVATAR_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(...)
}
)
def handle(self, context, inputs, output_definitions):
# 1. Accumulate text
context.text_buffer += inputs.data.get_main_data()
# 2. Check if there is a text end marker
if inputs.data.has_meta('text_end'):
# 3. Call the TTS API to generate audio
audio = edge_tts.generate(
text=context.text_buffer,
voice=self.voice
)
# 4. Output audio stream
for audio_chunk in audio:
yield ChatData(type=AVATAR_AUDIO, data=audio_chunk)
# 5. Clear the buffer
context.text_buffer = ""
Features:
▪️ Accumulates text and waits for a complete sentence
▪️ Supports multiple voices (selectable via configuration)
▪️ Outputs 24kHz audio
5.6 AvatarMusetalk Handler (Avatar Driving)
Function: Generates avatar video (lip-sync) from audio.
Input: ChatDataType.AVATAR_AUDIO (TTS-generated audio)
Output: ChatDataType.AVATAR_VIDEO (avatar video frames)
Key Code Location: src/handlers/avatar/musetalk/avatar_handler_musetalk.py
Key Methods:
def get_handler_detail(self, ...):
return HandlerDetail(
inputs={
ChatDataType.AVATAR_AUDIO: HandlerDataInfo(...)
},
outputs={
ChatDataType.AVATAR_VIDEO: HandlerDataInfo(...)
}
)
def handle(self, context, inputs, output_definitions):
# 1. Accumulate audio data
context.audio_buffer.append(inputs.data.get_main_data())
# 2. Check if there is an audio end marker
if inputs.data.has_meta('audio_end'):
# 3. MuseTalk model processing
video_frames = self.model(
audio=context.audio_buffer,
avatar_image=context.avatar_image
)
# 4. Output video frame stream
for frame in video_frames:
yield ChatData(type=AVATAR_VIDEO, data=frame)
# 5. Clear the buffer
context.audio_buffer.clear()
Features:
▪️ Precise lip-syncing
▪️ Supports 16fps video output
▪️ Uses the MuseTalk model for inference
5.7 Summary of the Handler Processing Chain
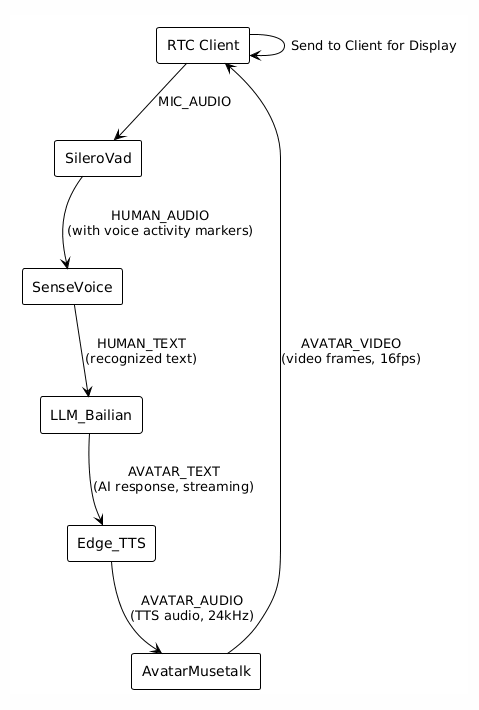
6. Quick Reference
6.1 Key Code Locations
| Function | File Path | Key Method |
|---|---|---|
| Main Entry | src/glut.py | main() |
| Engine Initialization | src/chat_engine/chat_engine.py | ChatEngine.initialize() |
| Handler Loading | src/chat_engine/core/handler_manager.py | HandlerManager.initialize() |
| Session Creation | src/chat_engine/chat_engine.py | ChatEngine.create_client_session() |
| Data Distribution | src/chat_engine/core/chat_session.py | ChatSession.distribute_data() |
| Input Processing | src/chat_engine/core/chat_session.py | ChatSession.inputs_pumper() |
| Handler Processing | src/chat_engine/core/chat_session.py | ChatSession.handler_pumper() |
6.2 Key Data Structures
Data Types (ChatDataType):
MIC_AUDIO # Microphone audio
HUMAN_AUDIO # Human speech audio
HUMAN_TEXT # User text
AVATAR_TEXT # AI response text
AVATAR_AUDIO # TTS audio
AVATAR_VIDEO # Avatar video
Data Routing Table (data_sinks):
data_sinks: Dict[ChatDataType, List[DataSink]]
# Data type → List of Handlers subscribed to this type
Handler Registry:
handler_registries: Dict[str, HandlerRegistry]
# Handler name → Handler registration info
6.3 Core Execution Flow
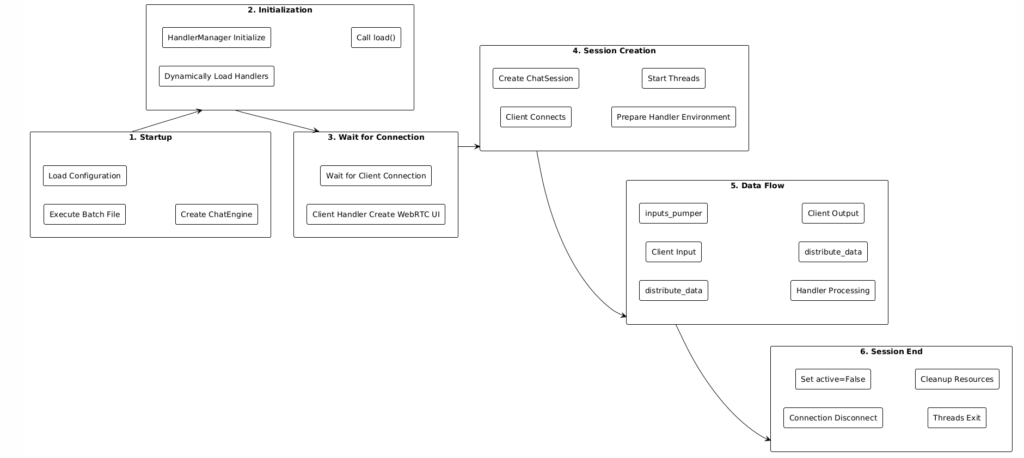
6.4 Key Features of Modularity
1. Configuration-driven: Define Handler combinations through YAML configuration files.
2. Dynamic Loading: Import and instantiate Handlers dynamically at runtime based on the configuration.
3. Data-driven Routing: Automatically distribute data based on data types, with Handlers unaware of each other.
4. Asynchronous Processing: Each Handler runs in its own thread, communicating via queues.
5. Loose Coupling: Handlers do not depend on each other directly, only on data types.
6. Easy to Extend: To add a new Handler, simply implement the HandlerBase interface.
7. Summary
OpenAvatarChat adopts a layered, modular architecture design:
▪️ Top Layer (ChatEngine): Manages the entire system and supports concurrent multi-session operation.
▪️ Middle Layer (ChatSession): Manages a single session and coordinates the collaborative work of Handlers.
▪️ Bottom Layer (Handler): Independent functional modules that communicate via data types.
Core Mechanisms:
▪️ Data Subscription: Handlers subscribe to data by declaring input types.
▪️ Automatic Routing: The system automatically distributes data based on data types.
▪️ Parallel Processing: Handlers run concurrently in independent threads.
▪️ Queue Communication: Communication between Handlers is asynchronous and decoupled via queues.
This design achieves a highly cohesive, loosely coupled architecture that makes the system easy to extend, maintain, and test.









Leave a Reply